World’s Smallest Autonomous Robots Developed, Operating at the Scale of Biological Cells
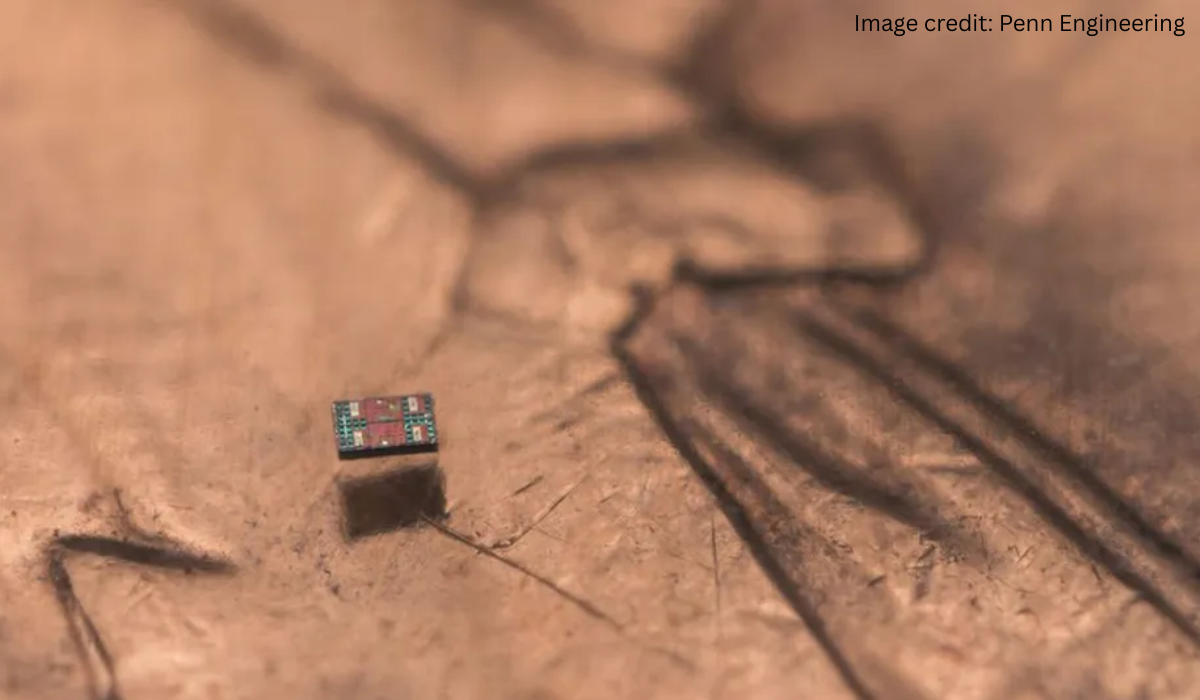
In a groundbreaking achievement, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan have unveiled what they describe as the world’s smallest fully autonomous robots. These microscopic devices, measuring just 200 × 300 × 50 micrometers – roughly one-tenth the width of a human hair – are capable of independent movement, environmental sensing, computation, and response, all without the need for external control, tethers, or magnetic guidance. This innovation opens up unprecedented possibilities for research and potential applications in fields ranging from medicine to materials science.
The development represents a significant leap forward in micro-robotics. Unlike previous iterations that relied on external power or control mechanisms, these robots are entirely self-contained. Each unit is designed for cost-effective manufacturing, with an estimated production cost of approximately one cent. This affordability is crucial for enabling large-scale experiments and potential future deployments.
Breaking Barriers in Miniaturization
The research, spearheaded in part by Marc Miskin, an assistant professor of electrical and systems engineering at the University of Pennsylvania, demonstrates a dramatic reduction in size compared to existing micro-robotic systems. “These robots operate at a scale comparable to many microorganisms,” explains Miskin, “allowing us to explore research avenues previously inaccessible due to size constraints.” Imagine being able to observe cellular processes from within, or manipulate materials at the nanoscale with unprecedented precision. What new insights into the fundamental building blocks of life might these robots reveal?
The findings have been published in two prestigious scientific journals: Science Robotics and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. These publications detail the intricate integration of power sources, computational logic, and movement mechanisms within a structure smaller than a grain of salt. The robots are engineered for extended operational lifespans, potentially functioning autonomously for months under optimal conditions.
Potential Applications and Future Outlook
While still in the experimental phase, the potential applications of these micro-robots are vast. Researchers envision their use in tracking the behavior of individual cells, studying microscopic environments with unparalleled detail, and even assisting in the construction of microscale machines. Their ability to function at the same physical scale as biological systems suggests the possibility of navigating complex tissues and lab-grown environments currently beyond the reach of conventional tools. Could these robots one day deliver targeted therapies directly to diseased cells, or repair damaged tissues from within?
It’s important to note that this research is a foundational step, a technical milestone rather than an immediately deployable technology. Consumer-facing applications remain theoretical, and practical implementation outside of laboratory settings is still years away. However, the progress demonstrated in miniaturization and autonomous control is undeniable, signaling a significant advancement in the field of robotics.
The Rise of Micro-Robotics: A Historical Perspective
The development of micro-robots has been a long-standing goal in the scientific community. Early attempts often faced limitations in power sources, control mechanisms, and manufacturing complexity. The breakthrough achieved by the University of Pennsylvania and University of Michigan teams lies in their ability to overcome these challenges through innovative design and materials science. This work builds upon decades of research in micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanotechnology, paving the way for even more sophisticated micro-robotic systems in the future.
The field is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in areas such as microfabrication, energy harvesting, and artificial intelligence. As these technologies continue to mature, we can expect to see micro-robots playing an increasingly important role in a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring to precision manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions About Micro-Robots
What are micro-robots?
Micro-robots are robotic devices with dimensions typically ranging from micrometers to millimeters. They are designed to operate in environments inaccessible to larger robots, such as inside the human body or within microscopic structures.
How are these micro-robots powered?
The current generation of these robots integrates power sources directly into their structure, allowing for autonomous operation without external power cables. The specific power source details are proprietary to the research team.
What is the primary application of these autonomous robots?
The primary application currently is research, specifically enabling scientists to study biological systems and microscopic environments at an unprecedented scale. Future applications could include targeted drug delivery and microsurgery.
How much do these micro-robots cost to produce?
Researchers estimate the cost of manufacturing each unit to be around one cent, making them remarkably affordable for large-scale experiments and potential future deployments.
Are these micro-robots ready for use in medical procedures?
No, these micro-robots are currently in the experimental stage. Significant further research and development are required before they can be safely and effectively used in medical procedures.
What challenges remain in the development of micro-robotics?
Challenges include improving power efficiency, enhancing control precision, developing robust sensing capabilities, and ensuring biocompatibility for medical applications.
The development of these autonomous micro-robots represents a pivotal moment in the field of robotics. As research progresses, we can anticipate even more remarkable advancements that will reshape our understanding of the microscopic world and unlock new possibilities for technological innovation. What ethical considerations should guide the development and deployment of such powerful technology?
Share this groundbreaking discovery with your network and join the conversation in the comments below!
Discover more from Archyworldys
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

